
How to save tax with PPF, NPS, and EPF
NPS and tax benefits play a vital role in this context, allowing taxpayers to not only reduce their tax liability but also make a strong financial plan for their retirement. The most popular tax-saving instruments include the Public Provident Fund (PPF), National Pension System (NPS) and Employees’ Provident Fund (EPF). These three schemes not only help individuals build a secure retirement corpus but also offer significant tax benefits.
Understanding NPS and Tax Benefits
NPS and tax benefits play a vital role in retirement planning and saving taxes. The National Pension System (NPS) is a government-funded pension scheme that offers several tax benefits under the Income Tax Act. Here’s how you can save taxes through NPS:
- Section 80CCD(1) Tax Deduction: Contributions to NPS qualify for a tax deduction of up to 10% of salary (salaried) or 20% of gross income (self-employed), capped at ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C.
- Additional deduction under section 80CCD(1B) – An additional deduction of ₹50,000 is available for contributions made to NPS, over and above the limit of ₹1.5 lakh under section 80C.
- Section 80CCD(2) Deduction: Employer’s NPS contribution (up to 10% of basic salary + DA) is deductible under Section 80CCD(2) and is tax-exempt.
- Tax-free growth potential benefits – At the time of retirement, 60% of the NPS corpus can be withdrawn tax-free, while 40% needs to be used to buy an annuity.
PPF and NPS tax benefits: A safe way to save tax
PPF and NPS Tax Benefits: PPF offers guaranteed returns, while NPS provides pension benefits. Together, they create a strong, tax-saving investment plan.
PPF and NPS Tax Benefits:
- Tax deduction under Section 80C – Employee contribution (up to 12% of salary) is eligible for tax deduction under Section 80C.
- Long term wealth creation – PPF has a lock-in period of 15 years (which can be extended in blocks of 5 years).
- .Safe and Guaranteed Returns – Being backed by the government, PPF is a safe and stable investment option.
- Exempt-Exempt-Exempt (EEE) Status – PPF comes in a completely tax-free category, i.e. contributions, interest earned and maturity amount are completely tax-free.
EPF: Tax-Efficient Retirement Plan
EPF is another excellent tax-saving option for salaried individuals. It is contributed by both the employer and the employee, leading to long-term wealth accumulation.
- Tax deduction under Section 80C – Employee contribution (up to 12% of salary) is eligible for tax deduction under Section 80C
- Employer contribution tax-free – Employer contribution (up to 12% of salary) is tax-free.
- Interest income tax-free – Interest earned on EPF is tax-free on contributions up to ₹2.5 lakh.
- Tax-free withdrawal after 5 years – If EPF is withdrawn after 5 years of continuous service, it is completely tax-free.
PPF, NPS or EPF: Which one to choose?
It depends on what your financial needs and risk appetite are. Here’s a quick comparison:
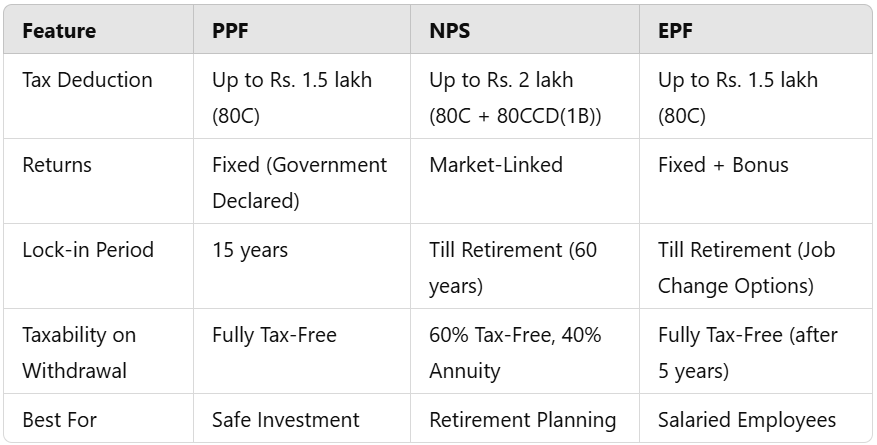
How to maximize tax savings from PPF, NPS, and EPF?
Follow the following strategies to avail maximum tax benefits from these schemes:
- Invest in NPS and use Section 80CCD(1B) – If you have met the limit of ₹1.5 lakh under Section 80C, invest more than ₹50,000 in NPS.
- Invest to get tax-free returns – PPF is the best option for long-term investment, providing completely tax-free interest income
- Take advantage of EPF – A salaried employee should contribute continuously to EPF so that he gets a tax-free corpus at the time of retirement.
- Use PPF and NPS tax benefit schemes properly – PPF gives security while NPS gives higher returns.





Pingback: How To Save Tax On Rental Income In India-2025 Save Tax On Rental Incime